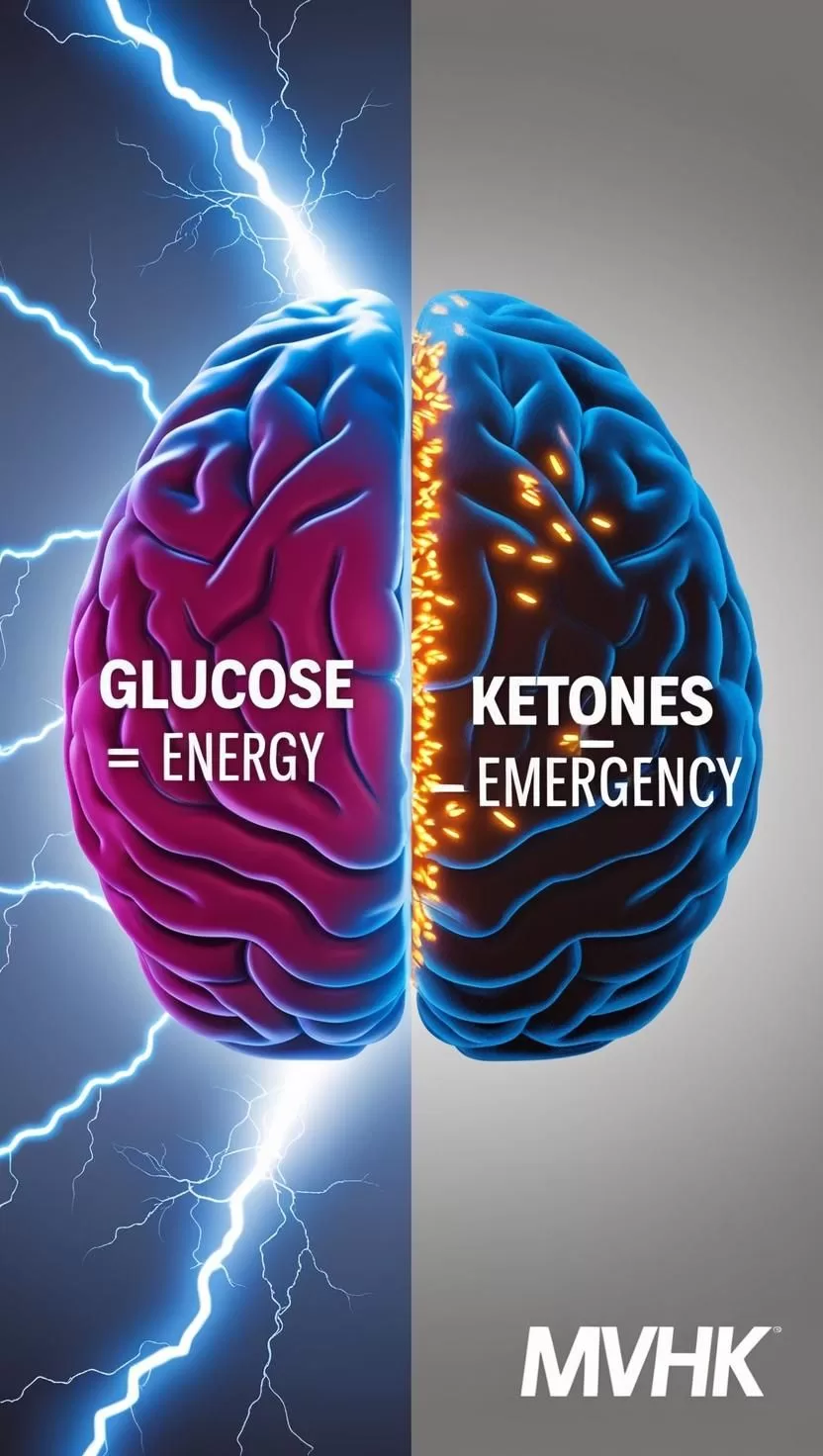
Can Ketones Truly Replace Glucose for Your Brain? Shocking Facts Revealed!
When it comes to brain fuel, most people believe that ketones are a powerful alternative to glucose. But here’s the surprising truth: your brain is designed to metabolize glucose over 99% of your life. Ketones only serve as a backup in emergencies like prolonged fasting or starvation. Let’s dig into the facts behind glucose vs. ketone metabolism and why it matters for your cognitive health.
1️⃣ Glucose: The Brain’s First Love
Why Glucose is Essential for Brain Function
Glucose is a simple sugar that provides quick and efficient energy. Your brain consumes roughly 20% of your total energy, even though it accounts for only 2% of your body weight.
Studies confirm that neurons rely almost exclusively on glucose for neurotransmission and synaptic activity (PubMed Study).
How Your Body Supplies Glucose
Even during fasting, your body can generate glucose via gluconeogenesis (from proteins and fats). This ensures the brain always has access to this crucial fuel.
2️⃣ Ketones: The Emergency Backup System
When and Why Ketones Are Produced
Ketones are synthesized in the liver when blood glucose levels fall critically low. Conditions that elevate ketone levels include:
- Extended fasting
- Starvation
- Strict ketogenic diets
- Uncontrolled diabetes
Ketones are not the body’s preferred fuel — they’re Plan B.
Limitations of Ketone Metabolism
Although ketones (like beta-hydroxybutyrate) can partially substitute for glucose, certain brain cells can’t use ketones effectively. Cognitive tasks, especially complex thinking and memory, function best with abundant glucose.
3️⃣ The Dangers of Overrelying on Ketosis
Cognitive Impairment Risks
Prolonged reliance on ketones can impair focus, mood stability, and executive function in some individuals.
Research shows that glucose-deprivation can lead to brain fog, irritability, and cognitive slowdown (Harvard Health Publishing).
Balancing Carbs and Brain Health
You don’t need high-carb diets — but smart carbohydrate intake from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is vital. Moderate, stable glucose levels support long-term brain performance.
Conclusion: How to Get Started Today
Fuel your brain intentionally!
- Prioritize complex carbohydrates.
- Avoid extremes like zero-carb diets unless medically necessary.
- Listen to your cognitive performance — if brain fog hits on keto, glucose may be the missing piece.
For more science-backed advice on nutrition and brain health, check out EverStayYoung.com!
Glucose and Brain Function – PubMed
FAQ
Can the brain survive on ketones alone?
No, certain brain cells still require glucose for optimal function, even during ketosis.
Is a ketogenic diet harmful for cognitive performance?
It can be for some people, especially if glucose levels fall too low to support memory and focus.
How can I support brain health naturally?
Consume balanced meals rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy carbs; avoid extreme dieting without medical supervision.